Step-by-Step Guide to Changing Sentence Structures
FAQs on Sentence Transformation Exercises: Simple, Compound & Complex
1. What is meant by the transformation of sentences in English grammar?
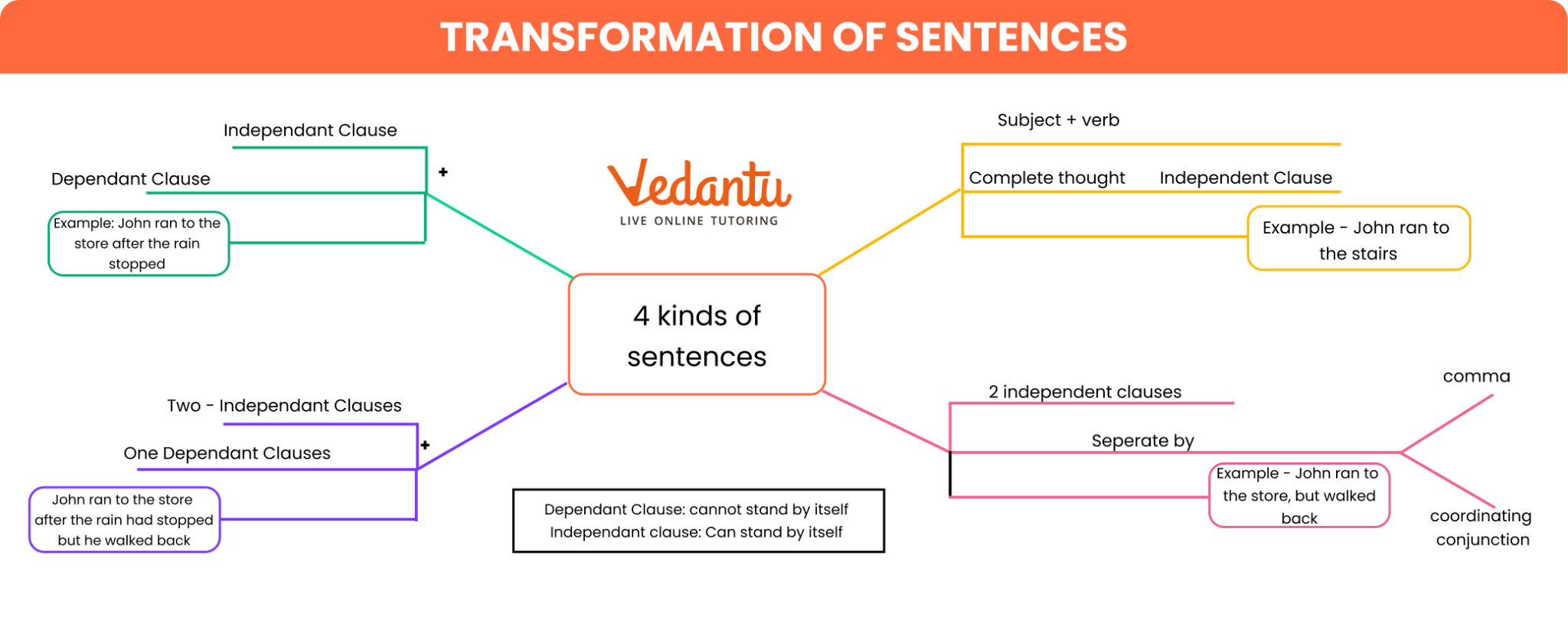
Sentence transformation is the process of changing a sentence's grammatical structure from one type (e.g., simple) to another (e.g., compound or complex) without altering its core meaning. This skill is fundamental for creating varied, sophisticated, and clear sentences in writing.
2. How do you transform a simple sentence into a compound sentence?
To change a simple sentence into a compound one, you must connect two independent clauses using a coordinating conjunction (like 'and', 'but', 'so', 'or', 'for'). For example, the simple sentence, "On seeing the teacher, the students stood up," can be transformed into the compound sentence, "The students saw the teacher, and they stood up."
3. What is the main difference between converting a sentence to a compound versus a complex structure?
The main difference lies in the type of clauses and conjunctions used.
- A compound sentence joins two or more independent clauses (of equal importance) with a coordinating conjunction (e.g., 'and', 'but').
- A complex sentence joins an independent clause with at least one dependent (subordinate) clause, showing a hierarchical relationship using a subordinating conjunction (e.g., 'because', 'although', 'since').
4. Can you give an example of transforming a complex sentence back into a simple sentence?
Yes. Consider the complex sentence: "Although he was poor, he was honest." To make it simple, we can replace the dependent clause "Although he was poor" with a phrase. The transformed simple sentence would be: "In spite of his poverty, he was honest." The structure is simplified while the meaning is preserved.
5. Why is learning to transform sentences important for CBSE students?
Learning sentence transformation is vital as it directly improves writing skills, which are tested across all sections of the English exam. It helps students write more dynamic and effective answers by avoiding repetitive sentence structures. This demonstrates a stronger command of grammar and allows for clearer expression of complex ideas, which can lead to higher marks.
6. What is a common mistake made when transforming sentences, and how can it be avoided?
A common mistake is creating a 'comma splice' when trying to form a compound sentence. This happens when two independent clauses are joined only with a comma, without a conjunction. For example: "She is intelligent, she works hard." This is incorrect. To avoid it, always insert a coordinating conjunction (e.g., "She is intelligent, and she works hard") or use a semicolon.
7. Does transforming a sentence ever change its original meaning?
The fundamental rule of sentence transformation is to preserve the original meaning. While the emphasis or nuance might shift slightly depending on the new structure, the core message must remain unchanged. If a transformation alters the essential information or the relationship between the clauses (e.g., changing cause to contrast), it is considered incorrect.