Types of Sentence Transformation with Examples and Practice Tips
FAQs on Transformation of Sentences Made Simple: Step-by-Step Guide
1. What is meant by the transformation of sentences in English grammar?
The transformation of sentences is the process of changing a sentence's grammatical structure or form without altering its fundamental meaning. This skill allows for expressing the same idea in various ways, for instance, by converting a simple sentence into a complex one, or an active voice sentence into a passive one.
2. Why is learning about sentence transformation important?
Learning sentence transformation is crucial as it significantly enhances writing versatility and communication skills. It deepens a student's understanding of grammatical structures and sentence logic, which is essential for constructing sophisticated, clear, and varied prose. This mastery is also frequently tested in academic and competitive examinations.
3. What are the main types of sentence transformations?
The primary types of sentence transformations involve changing a sentence's structure, voice, or mood. Common examples include:
Converting between Simple, Compound, and Complex sentences.
Changing an Affirmative sentence to a Negative one.
Transforming an Assertive (declarative) sentence into an Interrogative (question) or Exclamatory one.
Switching between Active Voice and Passive Voice.
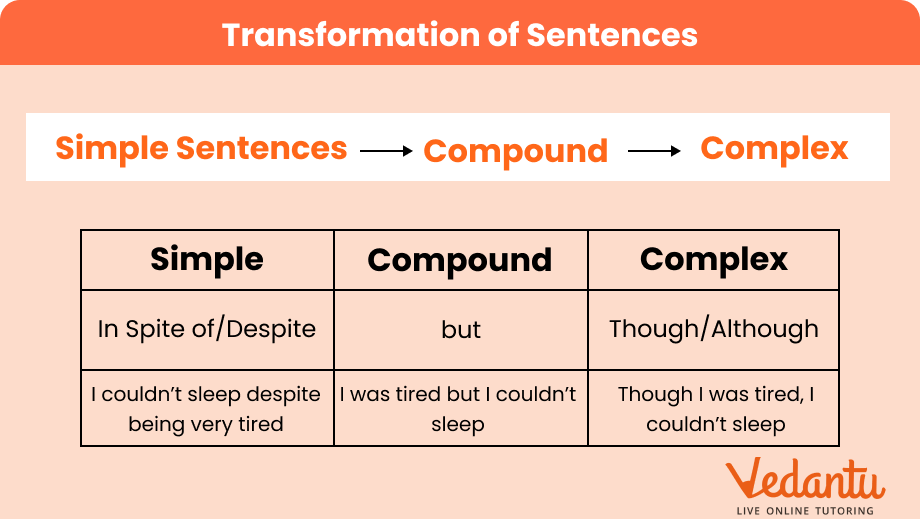
4. What is the difference between a simple, compound, and complex sentence?
The difference lies in their clause structure:
A simple sentence has only one independent clause (one subject and one verb).
A compound sentence contains two or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction like 'and', 'but', or 'or'.
A complex sentence has one independent clause and at least one dependent (subordinate) clause, connected by a subordinating conjunction like 'because', 'while', or 'since'.
5. Could you give an example of transforming a simple sentence into compound and complex forms?
Certainly. Consider the simple sentence: "He worked hard to pass the exam."
Compound Transformation: "He wanted to pass the exam, so he worked hard." (Two independent clauses joined by 'so').
Complex Transformation: "He worked hard so that he could pass the exam." (One independent clause and one dependent clause).
In both transformations, the core meaning remains unchanged.
6. Is it a rule that the meaning of a sentence must not change during transformation?
Yes, that is the most fundamental rule of sentence transformation. The entire objective is to alter the structure or form of the sentence while keeping its original meaning completely intact. If the meaning changes, the transformation is considered incorrect. For example, changing "He is a good boy" to "Is he not a good boy?" changes the form but preserves the affirmative meaning.
7. How does transforming a sentence from active to passive voice change its emphasis?
Changing from active to passive voice shifts the focus of the sentence. In the active voice (e.g., "The cat chased the mouse"), the emphasis is on the subject (the cat) performing the action. In the passive voice (e.g., "The mouse was chased by the cat"), the emphasis shifts to the object (the mouse) that receives the action. This transformation is useful when the action or the recipient of the action is more important than the doer.
8. What role do conjunctions play in the transformation of sentences?
Conjunctions are vital tools for transforming simple sentences into compound or complex ones. Coordinating conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) are used to join two independent clauses to create a compound sentence. Subordinating conjunctions (like although, because, since, while) are used to introduce a dependent clause, thereby creating a complex sentence.
9. Can all sentences be transformed into any other form?
Not necessarily. While most sentences can be transformed in some way (e.g., active to passive, affirmative to negative), not every sentence can be logically converted into all possible forms. For instance, a very simple sentence like "Birds fly" is difficult to turn into a meaningful complex sentence without adding new information. The feasibility of a transformation depends on the original sentence's components and the logical relationship between its ideas.
10. What are some common misconceptions when transforming sentences?
A common misconception is that transformation is just about swapping words. In reality, it requires a deep understanding of grammatical rules. Key mistakes stemming from this include:
Accidentally altering the tense of the sentence.
Using an incorrect conjunction that changes the logical relationship between clauses.
Creating a grammatically awkward or illogical sentence, especially when changing voice or sentence type.
The goal is always to maintain meaning and grammatical correctness.