




Overview of Solar and Lunar Eclipse
Eclipses have stimulated a number of scientific discoveries in addition to influencing artists and musicians. Solar eclipses have been used to study the structure of the Sun and its explosive events for more than a century. They have also been used to find support for the general relativity theory and to identify new elements.
NASA researchers continue to investigate eclipses in order to learn more about the Sun, Earth, and the space environment. Total solar eclipses are particularly significant because they provide scientists with a chance to observe the corona, a region of the Sun's atmosphere that is too weak to be seen against the Sun's brilliant brightness. Let’s find out more about them.
Solar and Lunar Eclipse for Kids
Lunar and solar eclipses are the two main categories into which they fall. Solar eclipses happen when the Moon moves in front of the Sun and Earth, casting a shifting shadow zone on the planet's surface. When Earth moves in front of the Sun and Moon, a lunar eclipse takes place, covering the Moon with a shadow.
Total solar eclipses, during which the Moon blocks out the Sun, are distinguished from annular eclipses, where the Moon only partially blocks out the Sun. The distance between such three objects determines whether an eclipse is partial or annular. The separation between any of these celestial bodies varies as a result of Earth's orbital path and the Moon's elliptical orbit around Earth.
The moon looks smaller in the sky than the sun when the sun is closest to earth, as well as the moon is at or around its greatest distance. In this case, the moon would not appear big enough to obscure the sun's disc totally, therefore, a rim or ring of lights will still be visible in the sky whenever an eclipse of the sun occurs. This eclipse is annular.
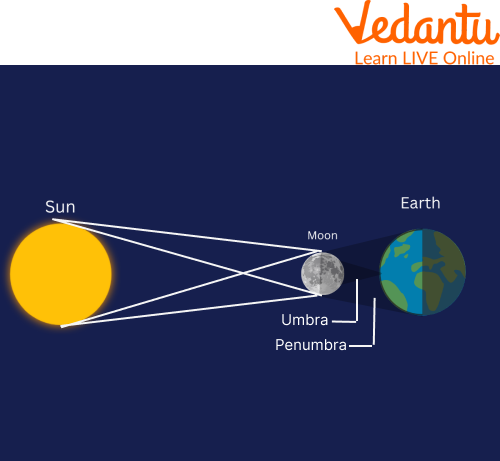
Simple Solar Eclipse
Facts About Solar Eclipse
Given below are some facts about solar eclipses, which will also be helpful in writing a Short Note on Solar Eclipse
The North and the South Poles are inaccessible during total solar eclipses.
Every 18 years and 11 months, nearly similar solar eclipses take place.
Depending on the Sun, Moon, and Earth's geometry, there may be two to five solar eclipses per year.
One to two years can pass between complete solar eclipses. They are, therefore, highly unusual occurrences.
The totality path typically spans an area of the Earth's surface around 10,000 miles long and has a width of about 160 km.
During a complete solar eclipse, if some planets are in the sky, they can be observed as points of light.
At new moon, a solar eclipse takes place. It is said to be new when the moon was between Sun and Earth. The new moon is the sole lunar phase during which that occurs.
Totality is a safe time to look. Observing the eclipse when the moon's disc is blocking the Sun is safe.

Solar Eclipse
Facts About Lunar Eclipse
Given below are some facts about the lunar eclipse, have a look!
Only a full moon causes a lunar eclipse.
The term "Syzygy" is used when the Earth, Sun, and Moon align.
There are three distinct types of lunar eclipses. You can have a total, partial, or penumbral moon eclipse.
The term "totality" is employed when the moon is totally dark.
During an eclipse, refraction makes the moon look red.
Lunar eclipses only happen occasionally. Lunar eclipses, of course, don't last forever.
Eclipses will vary from a few billion to several million years.
Christopher Columbus once escaped a jam by using his understanding of lunar eclipses.
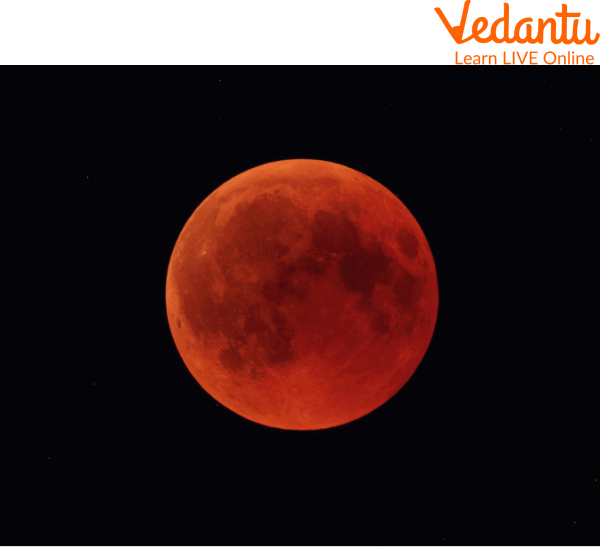
Lunar Eclipse
Summary
Solar eclipses have been used to study the structure of the Sun and its explosive events for more than a century. They have also been used to find support for the general relativity theory and to identify new elements. NASA researchers continue to investigate eclipses in order to learn more about the Sun, Earth, and the space environment. This article can be treated as a short note on solar eclipse. We studied solar and lunar eclipses and also saw some simple solar eclipse diagrams in this article.
Would a total solar eclipse, in which the moon totally blocks out the sun and plunges sections of the planet into absolute darkness for a few minutes, affect people physically, though? Simply put, no. NASA claims that there is no proof that human beings are physically impacted by eclipses.
FAQs on Solar and Lunar Eclipse for Kids
1. What are solar and lunar eclipses in simple terms for kids?
Think of the Sun, Earth, and Moon as friends playing hide-and-seek in space. A solar eclipse happens when the Moon moves between the Sun and Earth, hiding the Sun from our view for a short time. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth moves between the Sun and Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon and making it look dark or reddish.
2. What is the main difference between a solar and a lunar eclipse?
The main difference is the order of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. Here’s a simple breakdown:
Solar Eclipse: The Moon is in the middle (Sun-Moon-Earth alignment). It blocks the Sun’s light from reaching Earth.
Lunar Eclipse: The Earth is in the middle (Sun-Earth-Moon alignment). Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon.
3. How does a solar eclipse make the day turn dark?
During a total solar eclipse, the Moon lines up perfectly to block the Sun's entire face. Even though the Moon is much smaller than the Sun, it's also much closer to Earth, so it appears to be the same size in the sky. When it covers the Sun completely, its shadow falls on a small part of Earth, and for people in that shadow, the sky gets dark like it's night-time for a few minutes.
4. How does a lunar eclipse happen, and why does the Moon sometimes look red?
A lunar eclipse happens when the full Moon passes directly into Earth's shadow. This shadow has two parts: a lighter outer shadow (penumbra) and a darker inner shadow (umbra). When the Moon is fully inside the umbra, it can look reddish. This is because some sunlight still reaches the Moon by bending through Earth's atmosphere. Our atmosphere filters out most of the blue light, letting the red light pass through, which then illuminates the Moon. This is often called a 'Blood Moon'.
5. If the Moon orbits Earth every month, why don't we have eclipses all the time?
This is a great question! The reason we don't have eclipses every month is that the Moon's orbit around the Earth is slightly tilted. Imagine Earth's path around the Sun is a flat plate. The Moon's path is like another plate tilted at an angle. Because of this tilt, the Moon's shadow usually passes just above or below Earth, and Earth's shadow usually misses the Moon. Eclipses only happen on those rare occasions when all three align perfectly on the same level.
6. Why must you never look directly at a solar eclipse without protection?
It is extremely dangerous to look at a solar eclipse directly because the Sun's rays are incredibly powerful. Even when most of the Sun is covered, the remaining sliver can emit enough ultraviolet (UV) radiation to cause serious and permanent damage to your eyes, a condition called solar retinopathy. You should only ever view a solar eclipse through certified eclipse glasses or a special-purpose solar filter.
7. What are the different types of solar and lunar eclipses?
Eclipses can look different depending on how perfectly the Sun, Earth, and Moon line up. The main types are:
Types of Solar Eclipses: A Total eclipse is when the Moon completely blocks the Sun. A Partial eclipse is when it only blocks a part of the Sun. An Annular eclipse happens when the Moon is a bit farther from Earth and appears smaller, so it creates a bright 'ring of fire' around it.
Types of Lunar Eclipses: A Total eclipse is when the entire Moon enters Earth's darkest shadow. A Partial eclipse occurs when only a part of the Moon goes through the shadow. A Penumbral eclipse is very faint, as the Moon only passes through Earth's lighter outer shadow.
8. Why were people in ancient times scared of eclipses?
In ancient times, people did not have the scientific knowledge to understand what eclipses were. To them, the Sun was a source of life and light. Seeing it suddenly disappear during the day (a solar eclipse) or watching the Moon turn a dark, bloody red (a lunar eclipse) was a terrifying and mysterious event. Many cultures believed it was a bad omen or a sign that the gods were angry. Today, we know they are just a beautiful and natural alignment of shadows in space.









