




Overview of Distilling Flask
Kids, do you know what is distilling flask? You might not be familiar with the process distillation process, but a distillation flask is one of the most widespread devices used during the process. Distillation flasks can be found in labs, where they have used on a daily basis in various experiments. They are typically used for separating mixtures of different chemical components in labs.
In this article we will see how and why distilling flasks are important to us, we will also look at the uses of distilling flasks and the precautions we should take while using the distilling flask. So, let’s dive right in!
Applications of Distillation Flask
Distillation flasks are used in chemistry labs for various works. They are used to heat some mixtures of chemical compounds as it is impossible to heat them with bare human hands. They are generally made of glass because glass can bear high temperatures without breaking.
Distillation is a process in which a particular compound is taken out from a mixture by heating up the mixture in order to change the compounds from liquid to gaseous state. The change in the state happens from the lowest boiling point compounds to the highest boiling point compounds. And distillation flasks are widely used in this process.
Finding a distillation flask should not be difficult as they are widely sold at electronics stores or even online stores. There are even some places that can be rented or borrowed.
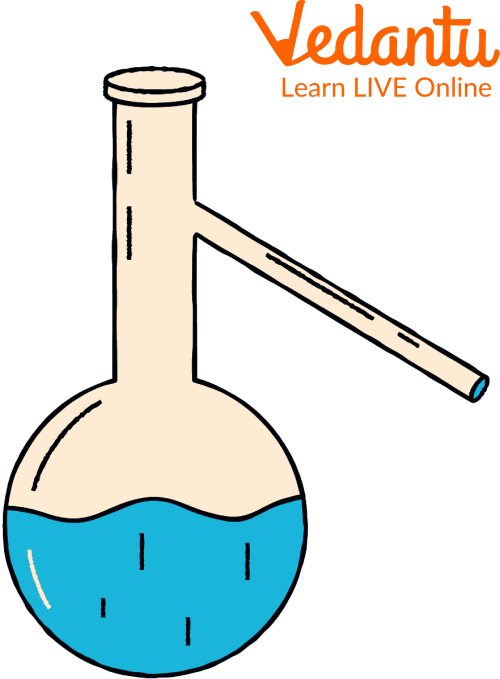
Distillation Flask
How Distillation Flask Works?
A distillation flask can be made of either glass, plastic or metal. It has a long neck, which is bent with a downward angle to prevent the volatile liquids from evaporating too early into the condenser. The bulbous bottom part houses the heating source, while the column-like part is used as a still pot in which volatile chemicals are distilled.
The liquid with the lowest boiling points vaporises first and gets condensed in the neck and later is collected in a separate container through the side arm. The side arm also makes adding more liquids to the flask easier. A thermometer can also be inserted in the neck of the flask so that the boiling points can be measured and recorded. Have a look at the distillation flask diagram given below.

Distillation Process
Uses of Distillation Flask in Everyday Life
Although the distillation flask mostly plays an important role in the scientific community, it can also be very useful in everyday life. The distillation flask is used in labs and industrial uses. The best part about it is that it is easy to use and can be used for various applications. Some of the everyday uses of distilling flask include:
It is used for teaching kids in science labs in schools and colleges. It is a widely used laboratory apparatus.
They are used to store various chemicals since some chemicals are dangerous, even in small quantities.
Precautions While Using Distilling Flask
Although using distilling may sound easy and interesting, it is a pretty tough task to catch up to. One should be aware of the harmful consequences of not using the distilling flask properly. So, let us learn how to be careful while using a distilling flask:
Always ensure that the connection joining the flask to the rest of the apparatus is properly and tightly secured.
Always clean the flask after using it, as the leftover chemicals may cause problems like they can mix up with the chemicals that are to be used in the next experiment.
Since the flask is usually made up of glass, make sure you do not break it while using it.
Summary
To conclude the above article, we would say that distilling flasks are crucial for science experiments. They help us with our experiments as we cannot use the chemicals with bare hands. But, with a distilling flask, it becomes easier. We should be very careful while using it; otherwise, we might cause serious problems due to minute negligence.
We would wrap up the article here, we have already discussed the uses and details of the distilling flask. We have also discussed the precautions that should be taken while using the flask, and in addition, we also looked at some distillation flask diagrams.
FAQs on Uses of Distilling Flask
1. What is a distilling flask and what is its primary function in a laboratory?
A distilling flask, also known as a distillation flask, is a piece of laboratory glassware specifically designed for the process of distillation. Its primary function is to hold a liquid mixture and heat it to its boiling point, allowing the component with the lower boiling point to vaporise before it is cooled and collected separately. It is a fundamental tool for purifying liquids and separating components of a mixture.
2. What are the main uses of a distilling flask in chemistry?
A distilling flask is used for several key separation techniques in chemistry. Its main applications include:
Simple Distillation: Separating a volatile liquid from a non-volatile solute, such as purifying salt water to get distilled water.
Fractional Distillation: Separating two or more miscible liquids with different boiling points, like separating ethanol from water.
Reaction Vessel: Containing chemical reactions that require heating or boiling under controlled conditions.
Steam Distillation: Extracting essential oils and other temperature-sensitive organic compounds.
3. Why is a distilling flask typically made from borosilicate glass?
Distilling flasks are made from borosilicate glass because it has two crucial properties for laboratory work. Firstly, it has a very high thermal shock resistance, meaning it can withstand rapid temperature changes and direct heating from a Bunsen burner without cracking. Secondly, it is chemically inert, so it does not react with the chemicals being heated inside it, ensuring the purity of the distillate.
4. How does a distilling flask differ from a Florence flask or an Erlenmeyer flask?
While all are common laboratory flasks, their designs are suited for different purposes. A distilling flask has a round bottom for uniform heating and a long neck with a side arm to direct vapour into a condenser. An Erlenmeyer flask has a flat bottom and a conical body, making it stable and ideal for swirling or mixing solutions without splashing. A Florence flask has a round body and a long neck but lacks the side arm, making it suitable for heating liquids but not for distillation.
5. What is the importance of the specific shape of a distilling flask?
The shape of a distilling flask is critical for its function. The round bottom ensures even and uniform heating of the liquid, preventing bumping and ensuring a smooth boil. The long neck minimises the risk of the boiling liquid splashing into the condenser. The side arm is positioned to efficiently channel the vapour out of the flask and into the condenser for cooling, which is essential for an effective separation process.
6. In what types of distillation processes is a distilling flask most essential?
A distilling flask is essential in any process that involves separating substances based on their boiling points. It is indispensable for:
Purification of Solvents: Removing impurities from solvents to obtain a pure liquid.
Crude Oil Refining: In a laboratory setting, fractional distillation in these flasks demonstrates how crude oil is separated into fractions like gasoline and kerosene.
Alcohol Production: Separating ethanol from the fermentation mash.
Water Purification: Creating distilled water for experiments by removing dissolved salts and minerals.
7. What other key apparatus is used with a distilling flask in a standard distillation setup?
A distilling flask does not work in isolation. For a complete distillation setup, it is used alongside other essential apparatus, including a heat source (like a Bunsen burner or heating mantle), a condenser to cool the vapour back into a liquid, a thermometer to monitor the temperature of the vapour, and a receiving flask (or beaker) to collect the purified liquid, also known as the distillate.









