Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Summary Notes PDF Download
FAQs on Temperature and its Measurement Class 6 Science Chapter 7 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is the main purpose of measuring temperature for a quick revision?
For a quick recap, the main purpose of measuring temperature is to determine the degree of hotness or coldness of an object. This is a crucial concept in science and has practical uses in daily life, such as checking for fever with a clinical thermometer or measuring the temperature of water in a science experiment with a laboratory thermometer.
2. How can you summarise the Celsius scale as a key concept?
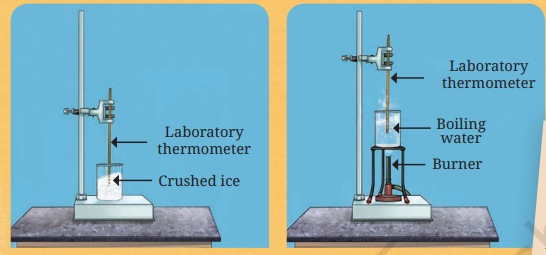
The Celsius scale is a common unit for measuring temperature, denoted by °C. For revision, remember its two primary reference points: the freezing point of water is 0°C, and the boiling point of water is 100°C. This scale is used worldwide for most scientific and everyday temperature measurements.
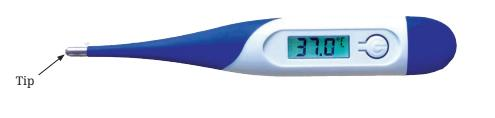
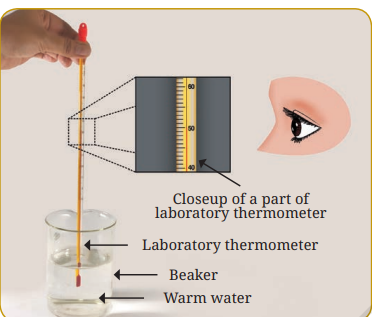
3. What are the key differences to remember between a clinical and a laboratory thermometer?
To revise this topic effectively, focus on these two main differences:
- Temperature Range: A clinical thermometer has a short range, typically from 35°C to 42°C, to measure human body temperature. A laboratory thermometer has a much wider range, such as -10°C to 110°C, for experiments.
- Design Feature: A clinical thermometer has a kink or constriction in the tube just above the bulb. This prevents the mercury level from falling back immediately, allowing time for an accurate reading. Laboratory thermometers do not have this kink.
4. What is the normal human body temperature that a Class 6 student should remember?
The average normal temperature for the human body is 37°C (thirty-seven degrees Celsius). It is important to recall that this is an average value, and a slight variation is perfectly normal.
5. What are the most important precautions to recall when using a laboratory thermometer?
While revising, focus on these key rules for using a laboratory thermometer correctly:
- It should be kept upright, not tilted.
- The bulb should be fully surrounded by the substance whose temperature is being measured.
- Ensure the bulb does not touch the surface or bottom of the container.
- Hold it by the glass stem, not the bulb, as your body heat can alter the reading.
6. Why is there a kink in a clinical thermometer but not in a laboratory one?
The kink is a crucial design feature specific to clinical thermometers. Its purpose is to prevent the mercury level from dropping on its own after the thermometer is removed from a patient's body. This gives a person enough time to note the reading accurately. A laboratory thermometer does not need this feature because the temperature is read while its bulb is still in contact with the substance.
7. Why does the temperature of pure water not increase beyond 100°C when it is boiling?
This is a core concept to understand. Once water reaches its boiling point of 100°C, any additional heat energy is used to change its state from liquid to gas (steam). This energy is used for the change of state rather than increasing the temperature. Therefore, the temperature of boiling water remains constant at 100°C.
8. Could you use a laboratory thermometer to check for a fever? Why is this not a good idea?
No, a laboratory thermometer is not suitable for checking body temperature. The key reason is its lack of precision for this purpose. Its temperature range is very wide, so the degrees are marked much closer together. This makes it very difficult to read the small, critical variations in body temperature that signify a fever (e.g., distinguishing between 37.5°C and 38°C).
9. Apart from being a visible silver liquid, what property of mercury makes it suitable for thermometers?
A key property of mercury that makes it ideal for thermometers is its uniform rate of expansion and contraction. This means it expands by the same amount for each degree rise in temperature. This ensures that the markings on the thermometer scale can be evenly spaced, leading to accurate and reliable readings.
10. How does the concept of 'temperature' connect to 'heat'?
For revision, it's important to understand the connection: Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is. Heat, on the other hand, is the form of energy that flows from a hotter object to a colder object. A difference in temperature between two objects is what causes this transfer of heat energy.